Understanding EAN-13 and EAN-8 Barcodes
Barcodes are used all over the world to make shopping, tracking, and inventory much faster and more accurate. Two of the most common barcode types are EAN-13 and EAN-8, especially in retail stores. In this blog, we’ll explain what they are, how they work, and where they’re used.
EAN-13 Barcode
1. What is an EAN-13 Barcode?
EAN-13 stands for European Article Number 13. It’s a barcode made up of 13 digits, used mainly to label and identify retail products worldwide. It’s managed by GS1, the global barcode standards organization.
2. Characteristics of EAN-13 Barcode
- Contains only numbers (0–9)
- Always 13 digits long
- Can be scanned from both directions
- Includes a checksum digit for error checking
- Used globally in retail and supply chain
3. Application of EAN-13 Barcode
EAN-13 barcodes are found on:
- Grocery items
- Books
- Medicine packaging
- Clothing tags
- Electronics
- Almost all products sold in supermarkets and stores
4. Structure of an EAN-13 Barcode
The 13-digit EAN-13 barcode is structured as follows:
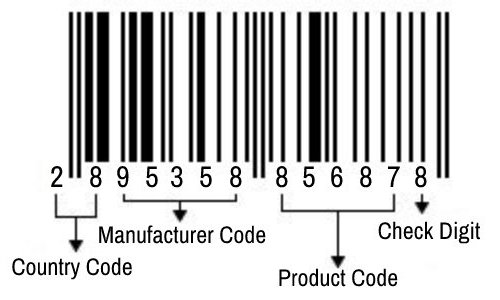
- GS1 Prefix: Indicates the country or region.
- Manufacturer Code: Assigned to the manufacturer.
- Product Code: Identifies the specific item.
- Check Digit: Used for error detection.
5. Encoding Method of an EAN-13 Barcode
The EAN-13 barcode is divided into three zones: left, center, and right.
- The first digit determines the parity pattern used for the next six digits on the left.
- The left-side digits use a mix of L-code (odd parity) and G-code (even parity).
- The right-side digits always use R-code (standard).
Encoding Table:
| Digit | L-code | G-code | R-code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0001101 | 0100111 | 1110010 |
| 1 | 0011001 | 0110011 | 1100110 |
| 2 | 0010011 | 0011011 | 1101100 |
| 3 | 0111101 | 0100001 | 1000010 |
| 4 | 0100011 | 0011101 | 1011100 |
| 5 | 0110001 | 0111001 | 1001110 |
| 6 | 0101111 | 0000101 | 1010000 |
| 7 | 0111011 | 0010001 | 1000100 |
| 8 | 0110111 | 0001001 | 1001000 |
| 9 | 0001011 | 0010111 | 1110100 |
The first digit (not encoded directly) defines the encoding pattern for the first six digits:
- For example, if the first digit is 0, the pattern is LLLLLL
- If it’s 1, the pattern is LLGLGG, and so on.
6. How to Calculate the Checksum of an EAN-13 Barcode
The checksum is the 13th digit and is used to verify that the barcode was scanned correctly.
Steps to calculate:
1. Starting from the left, add all digits in odd positions (1st, 3rd, 5th, etc.)
2. Add all digits in even positions (2nd, 4th, 6th, etc.) and multiply the sum by 3
3. Add both results.
4. Find the smallest number that makes the total a multiple of 10.
5. That number is the checksum.
Example:
Barcode (12 digits): 400638133393
- Odd positions: 4 + 0 + 3 + 1 + 3 + 9 = 20
- Even positions: 0 + 6 + 8 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 23 → 23 × 3 = 69
- Total = 20 + 69 = 89
- Checksum = 10 – (89 mod 10) = 1
Final EAN-13: 4006381333931
EAN-8 Barcode
What is an EAN-8 Barcode?
EAN-8 is a shorter version of the EAN-13 barcode. It encodes 8 digits and is used on small packages where a full-size barcode would not fit (e.g., pens, chewing gum, small cosmetics).
Characteristics of the EAN-8 Barcode
- Contains 8 digits: 7 data digits and 1 checksum digit.
- Also standardized by GS1.
- Compact size for limited packaging space.
Structure of an EAN-8 Barcode
An EAN-8 symbol is constructed in much the same fashion as an EAN-13, using the same start, center, and stop patterns. EAN-8 does not encode any of the data using parity; similar to a UPC-A, EAN-8 uses all odd parity characters for the first four digits and all even parity characters for the last four digits. Here is our original EAN-8 example, diagramed for clarity:
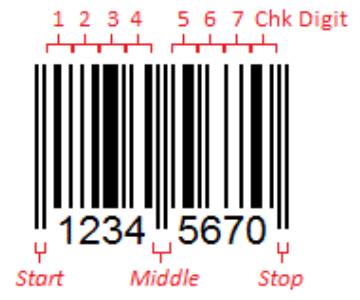
How it Works
- Encoded using similar L-code and R-code formats as EAN-13.
- The encoding method is symmetric with 4 digits on each side of a center guard pattern.
Checksum Calculation for EAN-8
Same method as EAN-13:
1. Sum digits in odd positions (1st, 3rd, 5th, 7th).
2. Sum digits in even positions and multiply by 3.
3. Add both.
4. Checksum = (10 – (sum mod 10)) % 10


